- Home
-
Learn
- History of VI >
- Legislation & Laws >
- Vision Professionals >
-
VI Program Resources
>
- Program Printables
- Itinerant Teaching Tips
- Year at a Glance
- VI Program Handbook
- Caseload Analysis
- Organization & Time Management
- Professional Development
- Teacher Standards
- Professional Ethics
- Awards & Recognition
- APH Scholar Program
- Professional Organizations
- Certification Organizations
- Dealing with Challenges
- Professional Publications >
- Relatable Books for All Ages >
- Family Resources >
- Plan
- Basics
-
Teach
- Teaching Strategies >
-
Compensatory Skills Instruction
>
-
Social Skills
>
-
Self Determination
>
- Body Image & Acceptance
- Making Personal Goals
- My Vision Presentation
- My Self-Description
- Create a Personal Data Sheet
- Disclosure Decision
- Disability Statement
- Requesting Help
- Fighting Fears
- My Circle of Support
- Personal Responsibility
- Advocate for Safe Enviroments
- Having Picture Taken
- Coping with Change
- Aging Eyes
- Physical Characteristics
- Political Activism
- Laws Regarding Persons with Disabilities
-
Sensory Efficiency
>
-
Independent Living
>
- Orientation & Mobility Instruction >
- Recreation & Leisure >
-
Career & Vocation
>
-
Grow
- Complete Set Bonus >
-
Recorded Presentations
>
- Webinar: Tips for Being a "Physically Fit" TVI
- Webinar: The Art of Teaching the ECC
- Webinar: Virtual & F2F Strategies
- Webinar: Foundations of Teaching the ECC in the Age of Virtual Instruction
- Webinar: Itinerant Teaching Strategies
- Webinar: Using Themes to Teach the ECC
- Webinar: Conducting a FVLMA
- Webinar: Selecting the Right AT
- Webinar: Developing SMARTER Goals
- Webinar: Determining Service Intensity Using the VISSIT
- Webinar: Activities to Teach the ECC
- Webinar: Accessible Content for BLVI
- Webinar: Accommodations for VI
- Webinar: MIMO Strategies & Activities
- Webinar: SIDPID Strategies & Activities
- Webinar: Standard Course of Study Strategies & Activities
- Webinar: Job Tasks for Job, Career & Life
- Shop
- Jobs
Impact on Development & LearningBy: Carmen Willings
teachingvisuallyimpaired.com Revised August 27, 2017 When a visual impairment is present from birth (congenital) it will have a more significant impact on development and learning that if the visual impairment is acquired later in life (adventitious). Loss of vision can affect all areas of development. Social development is affected as children are not able to pick up on non-verbal clues or if they are unable to make eye contact they may appear disinterested and can reduce sustained social interactions. Loss of vision impacts motor development as a child may not be motivated to move toward that which can't be seen or causes inhibition to move for fear of the unknown. Exploration of the environment and materials is critical in cognitive development, therefore movement is important not only for motor development but for the development of concepts. Language acquisition can also be affected by the loss of vision as active interaction with people and the environment is important in language development. Delays in the area of independence in activities of daily living are impacted as incidental learning through observation is not possible for those with significant visual impairments. This impact can be magnified when caregivers, in an effort to help or to rush through activities, complete tasks for the child which creates learned helplessness in the child.
Berthold Lowenfeld
Berthold Lowenfeld, a psychologist, researcher, and advocate for the blind hypothesized that blindness imposes 3 basic limitations on a person (often referred to as Lowenfeld Losses):
1. Loss of range and variety of experiences 2. Loss of the ability to get around 3. Loss of the control of the environment and the self in relation to it. Because of these restrictions, the individual relates to and learns about the world through the remaining senses, particularly hearing and touch. Lowenfeld stated that "A great many experiences which are taken for granted with seeing children are either impossible or much more difficult for blind children." Lowenfeld found that students with visual impairments required special experiences to help them make sense of what they were learning. Teachers need to make sure these are minimized through training and skills through active exploration with concrete materials. Read More about Berthold Lowenfeld at APH's Hall of Fame. Maslow's Hierarchy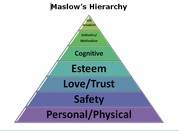
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a theory in psychology. It is often portrayed in the shape of a pyramid, with the largest and most fundamental levels of needs at the bottom, and the need for self-actualization at the top. Maslow's theory suggests that the most basic level of needs must be met before the individual will strongly desire the secondary or higher level needs. Maslow's hierarchy can be used to solve problems presented by the loss of vision.
"If you plan on being anything less than you are capable of being, you will probably be unhappy all the days of your life." |
History of Visual Impairments
Professional Practice
Vision Professionals
Professionalism
Teacher Resources
Professional Publications
VI Book Resources
Family Resources
VI Referrals
Medical vision exams
visual diagnosis
fvlma
|
|
Teaching Students with Visual Impairments LLC
All Rights Reserved |
- Home
-
Learn
- History of VI >
- Legislation & Laws >
- Vision Professionals >
-
VI Program Resources
>
- Program Printables
- Itinerant Teaching Tips
- Year at a Glance
- VI Program Handbook
- Caseload Analysis
- Organization & Time Management
- Professional Development
- Teacher Standards
- Professional Ethics
- Awards & Recognition
- APH Scholar Program
- Professional Organizations
- Certification Organizations
- Dealing with Challenges
- Professional Publications >
- Relatable Books for All Ages >
- Family Resources >
- Plan
- Basics
-
Teach
- Teaching Strategies >
-
Compensatory Skills Instruction
>
-
Social Skills
>
-
Self Determination
>
- Body Image & Acceptance
- Making Personal Goals
- My Vision Presentation
- My Self-Description
- Create a Personal Data Sheet
- Disclosure Decision
- Disability Statement
- Requesting Help
- Fighting Fears
- My Circle of Support
- Personal Responsibility
- Advocate for Safe Enviroments
- Having Picture Taken
- Coping with Change
- Aging Eyes
- Physical Characteristics
- Political Activism
- Laws Regarding Persons with Disabilities
-
Sensory Efficiency
>
-
Independent Living
>
- Orientation & Mobility Instruction >
- Recreation & Leisure >
-
Career & Vocation
>
-
Grow
- Complete Set Bonus >
-
Recorded Presentations
>
- Webinar: Tips for Being a "Physically Fit" TVI
- Webinar: The Art of Teaching the ECC
- Webinar: Virtual & F2F Strategies
- Webinar: Foundations of Teaching the ECC in the Age of Virtual Instruction
- Webinar: Itinerant Teaching Strategies
- Webinar: Using Themes to Teach the ECC
- Webinar: Conducting a FVLMA
- Webinar: Selecting the Right AT
- Webinar: Developing SMARTER Goals
- Webinar: Determining Service Intensity Using the VISSIT
- Webinar: Activities to Teach the ECC
- Webinar: Accessible Content for BLVI
- Webinar: Accommodations for VI
- Webinar: MIMO Strategies & Activities
- Webinar: SIDPID Strategies & Activities
- Webinar: Standard Course of Study Strategies & Activities
- Webinar: Job Tasks for Job, Career & Life
- Shop
- Jobs