- Home
-
Learn
- History of VI >
- Legislation & Laws >
- Vision Professionals >
-
VI Program Resources
>
- Program Printables
- Itinerant Teaching Tips
- Year at a Glance
- VI Program Handbook
- Caseload Analysis
- Organization & Time Management
- Professional Development
- Teacher Standards
- Professional Ethics
- Awards & Recognition
- APH Scholar Program
- Professional Organizations
- Certification Organizations
- Dealing with Challenges
- Professional Publications >
- Relatable Books for All Ages >
- Family Resources >
- Plan
- Basics
-
Teach
- Teaching Strategies >
-
Compensatory Skills Instruction
>
-
Social Skills
>
-
Self Determination
>
- Body Image & Acceptance
- Making Personal Goals
- My Vision Presentation
- My Self-Description
- Create a Personal Data Sheet
- Disclosure Decision
- Disability Statement
- Requesting Help
- Fighting Fears
- My Circle of Support
- Personal Responsibility
- Advocate for Safe Enviroments
- Having Picture Taken
- Coping with Change
- Aging Eyes
- Physical Characteristics
- Political Activism
- Laws Regarding Persons with Disabilities
-
Sensory Efficiency
>
-
Independent Living
>
- Orientation & Mobility Instruction >
- Recreation & Leisure >
-
Career & Vocation
>
-
Grow
- Complete Set Bonus >
-
Recorded Presentations
>
- Webinar: Tips for Being a "Physically Fit" TVI
- Webinar: The Art of Teaching the ECC
- Webinar: Virtual & F2F Strategies
- Webinar: Foundations of Teaching the ECC in the Age of Virtual Instruction
- Webinar: Itinerant Teaching Strategies
- Webinar: Using Themes to Teach the ECC
- Webinar: Conducting a FVLMA
- Webinar: Selecting the Right AT
- Webinar: Developing SMARTER Goals
- Webinar: Determining Service Intensity Using the VISSIT
- Webinar: Activities to Teach the ECC
- Webinar: Accessible Content for BLVI
- Webinar: Accommodations for VI
- Webinar: MIMO Strategies & Activities
- Webinar: SIDPID Strategies & Activities
- Webinar: Standard Course of Study Strategies & Activities
- Webinar: Job Tasks for Job, Career & Life
- Shop
- Jobs
Writing SMART GoalsBy: Carmen Willings
teachingvisuallyimpaired.com Revised November 20, 2018 Individualized Education Program (IEP) formats and the criteria vary greatly between states and sometimes within states and even counties! One thing in common is that all goals should be "S.M.A.R.T.". "S.M.A.R.T." goals should meet the student's needs that result from the student's disability to enable the child to be involved in and make progress in the general education curriculum, and meet each of the student's other educational needs that result from the student's disability. Goals are goals that are: 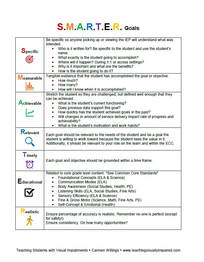
Specific
A specific goal has a much greater chance of being accomplished than a general goal. To set a specific goal you must answer the six "W" questions:
Blooms Taxonomy of cognitive objectives can be helpful when determining the "action" word to describe what the student must do to meet the goal. Measurable Establish concrete criteria for measuring progress toward the attainment of each goal. What tangible evidence that the student has accomplished the goal or objective. When you measure your progress, you stay on track, and reach your target dates. To determine if the goal is measurable, ask questions such as:
Achievable/Attainable Set a plan and establish a time frame that allows you to carry out those steps. Stretch the student so they are challenged, but defined well enough that they can be achieved.
Realistic & Relevant To be realistic, a goal must represent an objective toward which you are both willing and able to work. A goal can be both high and realistic. Be sure that every goal represents substantial progress. Additionally, it should be relevant to your role on the team and within the ECC. Timely A goal should be grounded within a time frame. With no time frame tied to it, there's no sense of urgency. Ex. When asked to complete a written assignment, (name), will independently load the paper in the braille writer with 90% accuracy on 4 of 5 opportunities by the end of the IEP duration. The 3 C'sShort-term objectives (or benchmarks) must also be SMART and contain the 3 C's: condition; clearly defined behavior; performance criteria. Objectives describe the small steps needed to achieve the goal.
|
History of vi
Visual Impairments
Vi organizations & Agencies
VI book resources
VI Professionals
Professionalism
Instructional Planning
Professional Publications
Educational Programming
Individual Learning Differences
referrals
Medical vision exams
fvlma
additional evaluations
service planning
writing goals
compensatory skills
Guiding Principles Functional Skills Community Based Experiences Concepts to Teach Access to Instruction Organization & Study Skills Time Management Virtual Instruction Movies & Assemblies Lectures & Instruction Board Work (Chalk, White, etc.) Daily Schedule Morning Meeting Weather Check Dramatic Play Blocks Numbers & Counting Cranmer Abacus Instruction Algebra Geometry & Spatial Sense Measurement & Data Early Literacy Experiences Create Tactual Books Reading Instruction Reading Efficiency Science Adaptations Social Studies Adaptations Communication Modes Accessible Educational Materials Individual Schedules & Communication Cards Adjust Lighting Large Print Optical Devices for Near Optical Devices for Distance Optical Device Use Photocopying Font Legibility Increase Contrast Pictures & Worksheets Keyboarding Instruction Word Processing and Shortcuts Navigate Computer w/o a Mouse Braille Code Braille Instruction Braille Instruction Materials Writing Braille Summer Reading (braille) Signature & Handwriting Nemeth Braille Code Tactile Graphics Guidelines Creating Tactile Graphics Tactile Graphics Instruction Teacher Made Materials Labeling System assistive technology
Overview of Assistive Technology VI AT Resources Non-Optical Low Vision Devices Video Magnifiers Video Magnifier Instruction Screen Enlargement & Readers Low/Med. Tech Tactual Devices Notetaker Instruction Braillewriter Repair Tactile Graphics Technology Braille Technology Auditory Access Devices Accessing Audio Books iPads as Instructional Tools Making iOS Device Accessible iOS Accessibility Resources VoiceOver Apps for VI Note Taking apps Apps for Accessing Books Identification Apps Navigation & Location Apps Braille Apps Magnifier Apps Sound Making Apps Cause & Effect Apps Vision Skills Apps Apps for Early Learning Read to Me Story Apps Apps for Communication Android Apps for VI sensory efficiency
Sensory Input Encourage Use of Vision Sensory Area & Rooms Lightbox Use Sensory Activities for Students with Multiple Disabilities Sensory Tables Visual Efficiency Skills Visual Attend and Scan Activities Visual Tracking Activities Visual Discrimination Activities Visual Motor Activities Tactual Readiness Developing Skillful Hands Auditory Readiness Listening Skill Instruction independent living
orientation & Mobility
career education
recreation & Leisure
self determination
|
|
Teaching Students with Visual Impairments LLC
All Rights Reserved |
- Home
-
Learn
- History of VI >
- Legislation & Laws >
- Vision Professionals >
-
VI Program Resources
>
- Program Printables
- Itinerant Teaching Tips
- Year at a Glance
- VI Program Handbook
- Caseload Analysis
- Organization & Time Management
- Professional Development
- Teacher Standards
- Professional Ethics
- Awards & Recognition
- APH Scholar Program
- Professional Organizations
- Certification Organizations
- Dealing with Challenges
- Professional Publications >
- Relatable Books for All Ages >
- Family Resources >
- Plan
- Basics
-
Teach
- Teaching Strategies >
-
Compensatory Skills Instruction
>
-
Social Skills
>
-
Self Determination
>
- Body Image & Acceptance
- Making Personal Goals
- My Vision Presentation
- My Self-Description
- Create a Personal Data Sheet
- Disclosure Decision
- Disability Statement
- Requesting Help
- Fighting Fears
- My Circle of Support
- Personal Responsibility
- Advocate for Safe Enviroments
- Having Picture Taken
- Coping with Change
- Aging Eyes
- Physical Characteristics
- Political Activism
- Laws Regarding Persons with Disabilities
-
Sensory Efficiency
>
-
Independent Living
>
- Orientation & Mobility Instruction >
- Recreation & Leisure >
-
Career & Vocation
>
-
Grow
- Complete Set Bonus >
-
Recorded Presentations
>
- Webinar: Tips for Being a "Physically Fit" TVI
- Webinar: The Art of Teaching the ECC
- Webinar: Virtual & F2F Strategies
- Webinar: Foundations of Teaching the ECC in the Age of Virtual Instruction
- Webinar: Itinerant Teaching Strategies
- Webinar: Using Themes to Teach the ECC
- Webinar: Conducting a FVLMA
- Webinar: Selecting the Right AT
- Webinar: Developing SMARTER Goals
- Webinar: Determining Service Intensity Using the VISSIT
- Webinar: Activities to Teach the ECC
- Webinar: Accessible Content for BLVI
- Webinar: Accommodations for VI
- Webinar: MIMO Strategies & Activities
- Webinar: SIDPID Strategies & Activities
- Webinar: Standard Course of Study Strategies & Activities
- Webinar: Job Tasks for Job, Career & Life
- Shop
- Jobs